What is a wetland?
Wetlands are lands transitional between terrestrial and aquatic systems where the water table is usually at or near the surface or the land is covered by shallow water. For purposes of this classification, wetlands must have one or more of the following three attributes: (1) at least periodically, the land supports predominantly hydrophytes, (2) the substrate is predominantly undrained hydric soil, and (3) the substrate is nonsoil and is saturated with water or covered by shallow water at some time during the growing season of each year (Cowardin et al. 1979).
OR, in simpler terms, a site must have wetland plants, soil with indicators of formation under wet conditions, and/or regular wetness at least during the spring each year to be considered a wetland.
In Nevada, we have a large diversity of wetlands including springs, riparian areas, fens, meadows, playas, marshes, vernal pools, and ephemeral washes. All types of wetlands provide critical habitat for plants and animals.
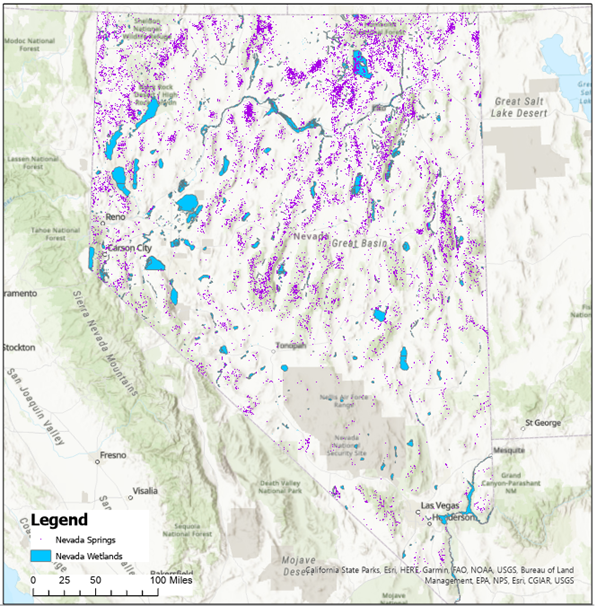
2023 Nevada Priority Wetlands Inventory - This project sought to identify some of the most valuable and threatened wetland habitats in Nevada that should be the highest priority for conservation, whether in the form of restoration, preservation, or regulatory protections.
